
Today, we are discussing Banana Tissue Culture to provide step by step guide to plant tissue culture in bananas.
How can we define Tissue culture? Well, Tissue culture is a process of cloning and micropropagation of tissues of the selected quality plants & daughter suckers or Tissue culture is the modern technology that can be applied for mass production of superior grade planting material for most crops. This method of cultivation or production ensures not only higher yields but quality as well. The Tissue culture technology is composed of 5 important steps as Initiation, Multiplication, Shooting & rooting, Primary hardening in a greenhouse, and Secondary hardening in shade net houses. To be successful in the Tissue culture method, one should adhere to standards, and micro-climatic conditions & care during the hardening process can ensure success.

Usually, the banana crop is being propagated by vegetative means (method) such as suckers and bits. However, Banana trees can easily adapt to tissue culture technology in the laboratory. The banana mother plant material used in the Tissue culture method is from areas that have recorded disease-free cropping for many years. In the clonal selection process of tissue culture, healthy, high-yielding, quality, and vigorous donor banana plants of desired varieties (cultivars) are identified. As part of the initiation of Tissue culture, the Meristem tissue portion of the bud is teased out from the basal corm of donor banana plants, surface-sterilized & inoculated to on artificial nutrient media. Due to rapid cell division in the meristem region, it is devoid of systemic microbes, especially viruses & viroids (smallest infectious pathogens).
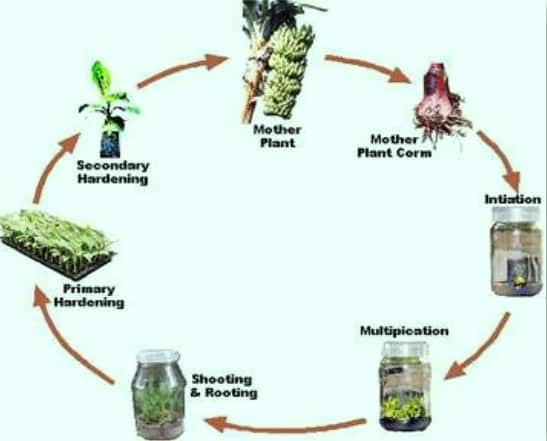
The initiated tissue will be disease-free and in a controlled environment of a laboratory which can be multiplied several folds to obtain the required number of each banana variety (cultivar) depending upon the market demand. Subsequently, the rooted banana tissue plants are released from the laboratory to a climate-controlled environment such as a greenhouse for acclimatization. This requires 8 to 13 weeks to complete the primary hardening process. The hardened plantlets of banana will have 4 to 5 leaves and a well-developed root system at the end of the period. Secondary hardening of plants can be hardened in secondary controlled environments such as shade houses /shade nets. In the following article, let us discuss more “Banana Tissue Culture” Process and cultivation.
There are several benefits of using tissue-cultured banana plantlets when compared to regular (conventional) suckers.
If the selected area has an irrigation facility banana cultivation can be carried out throughout the year. It is recommended to adjust the secondary nursery planting to before monsoon (pre-monsoon) in order to coincide with the monsoon season in that particular region. When it comes to the tissue culture of bananas, there are two types of Tissue culture plants are available.

Grading:
You must grade the plants based on their height and girth before planting in the main field.
After growing for 8 to 12 weeks of the secondary nursery, they should be transplanted to the main field. There is no need to cut back the pseudo-stem (the part of the banana plant that looks like a trunk) for tissue culture banana plantlets in polybags.

Give a couple of ploughings to get the soil to the fine tilth stage and weed-free. Soil test and analysis for lime and phosphate is essential before planting the tissue culture plantlets. Pits to be dug for transplanting the material.
Spacing generally depends on cultivar/variety and planting method. In the case of Dwarf varieties, it requires spacing of 5.5 feet x 5.5 feet and plant density (Number of plants) required is about 1400 to 1450/acre. Red banana variety requires 8 ft. x 8 ft. and plant density would be around 700/acre. There are other banana varieties like Giant Cavendish, Nendran, Robusta, and Grandnaine, Williams requires spacing from 6 feet x 6ft – 7 feet x 7feet and no plants required per acre are from 900 to 1200. Do not plant too shallow or too deep and allow a space of 10 cm between the plant and the soil surface.
The frequency of irrigation depends on soil moisture-holding capacity and climate. For proper utilization of water in tissue culture planting, it is recommended to adopt drip irrigation. Irrigate the Banana plantation immediately after planting in the field. There is a government subsidy for drip irrigation as well. Usually, a Banana plant requires 20 to 25 liters of water per day under a drip irrigation system . In hot summers or dry spells, it is a good practice to give flood irrigation once a month apart from using the drip system.
The schedule of manures and fertilizers in Tissue culture plantations depends on soil fertility. Based on soil test results, appropriate manures and fertilizers should be applied. However, the following manures and fertilizers gave for your reference.
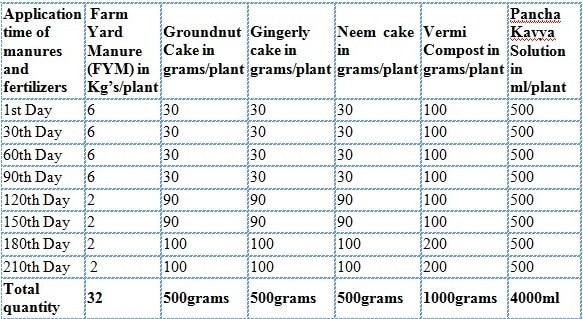
As we already mentioned that Tissue culture banana plants are disease-free at the time of planting. One can grow the Banana crop without any pest disease incidence with good crop management practices. However, to avoid any pest and disease incidents, you can apply 400 to 450 grams of Neem cake along with pit mixture before transplanting in the field. Neem oil or Panchagavya solution can be applied in the second and third months of the crop stage.

Carrying intercultural operations such as weeding and earthing is essential in crop systems. Weeds can be controlled by hoe and hand. Make sure the Banana field is weed-free and remove any side suckers of the Banana plant during the cropping stage. Earthing up should be carried out 90 to 100 days after transplantation. This should be done after the application of Neem cake and farmyard manure. Once the Banana fruit bunch is formed, the terminal male flowers with the bracts should be cut off. Protect the plants from lodging due to strong winds and heavy fruit-bearing. This can be done by propping the bunches with a rope and sticks.
The following is the flow chart of Banana Tissue Culture Technology.

The cost of tissue-cultured banana plants depends on age and variety. For example, G9 tissue culture banana plants cost per net pot plant is Rs. 10 excluding Transport cost. These plants have been hardened for 45 days. in general, the price may vary from 8 to 12 Rs.